Overview
Learn about background tasks & cron jobs and how they can power your application.
Background tasks and cron jobs are long-running processes that execute outside of your main application flow, allowing you to handle time-intensive operations and scheduled workflows without blocking user interactions or hitting serverless function timeouts.
Perfect for time-intensive & scheduled operations
Background tasks are ideal for operations that take longer than typical serverless function timeouts (10-60 seconds), such as processing large files, sending batch emails, or making multiple API calls.
Cron jobs are perfect for recurring operations like daily reports, cleanup tasks, or periodic data synchronization.
What are background tasks?
Background tasks are asynchronous processes that run separately from your main application thread. Instead of forcing users to wait for lengthy operations to complete, you can offload these tasks to run in the background while your application remains responsive.
Cron jobs are scheduled background tasks that run automatically at specific times or intervals. They're perfect for maintenance operations, reports, and recurring workflows that need to happen without user intervention.
Think of background tasks as your application's worker threads - they handle the heavy lifting while your main application stays fast and responsive for users.
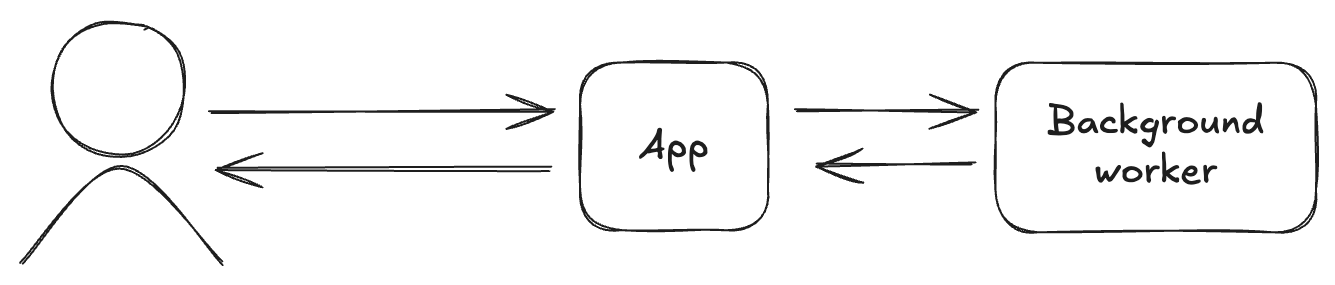
Why use background tasks?
Avoid timeouts
Most serverless platforms have strict execution limits:
- Vercel (Hobby): 300 seconds
- Vercel (Pro): 800 seconds
- Vercel (Enterprise): 800 seconds
- AWS Lambda: 900 seconds
- Netlify Functions: 30 seconds
Background tasks let you bypass these limitations entirely.
Better user experience
Users don't have to wait for long-running processes. They can continue using your application while tasks complete in the background.
Automated workflows
Cron jobs enable hands-off automation of recurring tasks like daily backups, weekly reports, or monthly user engagement analysis - all running reliably without manual intervention.
Improved reliability
Background tasks can be automatically retried if they fail, ensuring your critical processes eventually complete successfully.
Resource optimization
Your main application servers stay available to handle user requests instead of being tied up with heavy processing tasks.
Common use cases
Here are some typical scenarios where background tasks shine:
- Video transcoding: Converting uploaded videos to different formats or resolutions
- Image optimization: Batch processing user-uploaded images
- Document parsing: Extracting text from PDFs or generating thumbnails
- Database migrations: Moving or transforming large datasets
- Report generation: Creating complex analytics reports
- Data synchronization: Syncing data between different systems
- Email campaigns: Sending personalized emails to large user lists
- Notification processing: Delivering push notifications across multiple platforms
- SMS campaigns: Bulk SMS sending with rate limiting
- Content generation: Using AI models to generate text, images, or videos
- Data analysis: Running machine learning models on large datasets
- Natural language processing: Analyzing text content for insights
- API synchronization: Syncing data with external services
- Webhook processing: Handling incoming webhooks that trigger complex workflows
- Social media automation: Posting content across multiple platforms
- Daily reports: Generating and emailing daily analytics or performance reports
- Database maintenance: Cleaning up old records, optimizing indexes, or running backups
- User engagement: Sending weekly newsletters or monthly account summaries
- System monitoring: Health checks, performance monitoring, and alert notifications
- Content management: Auto-publishing scheduled content or archiving old posts
When not to use background tasks?
Background tasks and cron jobs aren't always the right solution. Consider alternatives for:
- Real-time operations: Tasks that users need immediate results from
- Simple, fast operations: Tasks that complete in under 5-10 seconds
- Database queries: Standard CRUD operations that should remain synchronous
- User authentication: Login/logout processes should be immediate
Keep it simple
Start with synchronous processing for simple tasks and manual processes for infrequent operations. Only move to background tasks when you hit timeout limitations or user experience issues, and only use cron jobs when you need reliable automation.
Getting started
Ready to add background tasks to your TurboStarter application? Check out our Trigger.dev integration guide or Upstash QStash integration guide to learn how to implement background tasks using one of the most developer-friendly background job frameworks available.
How is this guide?
Last updated on